What You Need to Know About Melanoma
June 30, 2018
What You Need to Know About Melanoma
Skin cancer is by far the most common type of cancer in the U.S. According to the American Academy of Dermatology, one in five Americans will develop some form of skin cancer in their lifetimes. Skin cancer comes in different types, with melanoma and non-melanoma being the main two categories.
Non-melanoma skin cancers affect over 3 million Americans each year, while melanoma impacts over 1 million Americans. The good news is that with early detection, both non-melanoma and melanoma skin cancers are highly treatable and curable.
However, without early detection, melanoma can be deadly. According to the American Cancer Society, the survival rate when melanoma is detected early is 99 percent. It falls to 63 percent when the cancer reaches the lymph nodes and 20 percent when the cancer metastasizes into the organs.
Here is what you need to know about this potentially deadly form of skin cancer.
Risk Factors
While melanoma can occur in almost anyone, a few things can increase your risk of developing this form of skin cancer. Here are a few risk factors to be aware of:
- Exposure to UV light. One major risk factor for melanoma is regular exposure to ultraviolet (UV) rays. UV rays come from both sunlight and the light produced by tanning beds and damage your skin cell's DNA. Reducing your exposure to harmful UV rays can reduce your skin cancer risk.
- A history of sunburns. Even if you are not exposed to UV rays on a regular basis, just a few sunburns can increase your chances of getting melanoma.
- Family history. Having a close relative who has dealt with melanoma may also mean that you are at an increased risk of developing it as well.
- Hair and skin color. While melanoma can occur in anyone regardless of skin and hair color, those will fair skin, green or blue eyes, red or blonde hair, or skin that freckles easily are at an increased risk.
- Age. Your age is another factor that can impact your risk of melanoma. As your age increases, so do your chances of developing melanoma. The older you are, the more exposure you have had to UV rays.
Being aware of these risk factors and taking precautions is key.
Tell-Tale Signs
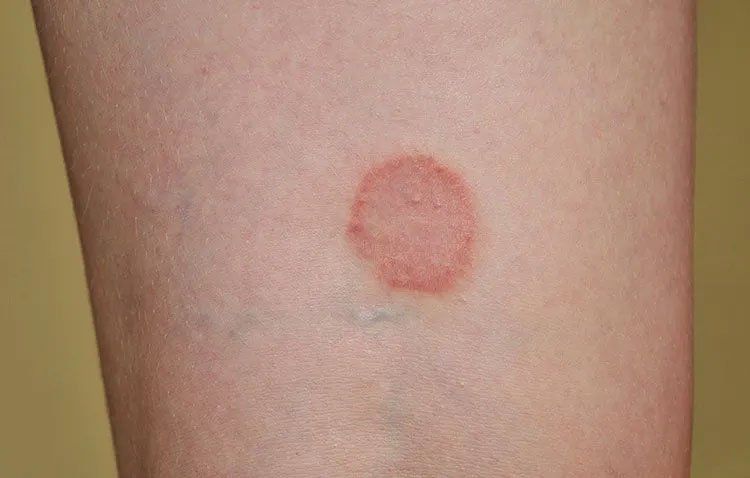
You should also know the signs of melanoma. When it comes to moles, the American Cancer Society suggests the very helpful ABCDE rule. In moles you want to look for these attributes that may signal melanoma:
- Asymmetry. If one side of the mole does not match the other, it's asymmetrical and may be a sign of melanoma.
- Border. An irregular border that is jagged or blurred may also be a sign of melanoma.
- Color. Non-uniform coloration of your moles may also be a warning sign.
- Diameter. Size is also important. Moles larger 6 millimeters across can be a sign of melanoma.
- Evolving. Another potential sign of melanoma is if your moles experience changes in terms of size, shape, or color.
Other signs that you need to pay attention to that may indicate melanoma include sores that will not heal, redness and swelling of the skin, and itchiness or pain.
Prevention and Diagnosis
When it comes to melanoma, prevention is key. Dermatologists recommend avoiding direct sunlight, wearing sunscreen, and taking other protective measures when outside, as well as avoiding tanning beds and sunlamps. Regular self-screenings are also essential. If you notice any changes to your moles or your skin, a visit to the dermatologist is a must.
In order to diagnose melanoma, your dermatologist will first perform a visual exam followed by a biopsy of any suspicious areas. If melanoma is present, a doctor can treat it through surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, or immunotherapy depending on your needs.
When left untreated, melanoma can be deadly, which is why you need to see your dermatologist as soon as possible if you notice any changes in your skin. If you have any concerns or have noticed any signs that may point to melanoma, contact
Spartanburg Dermatology & Skin Surgery Clinic, P.C., for an appointment.
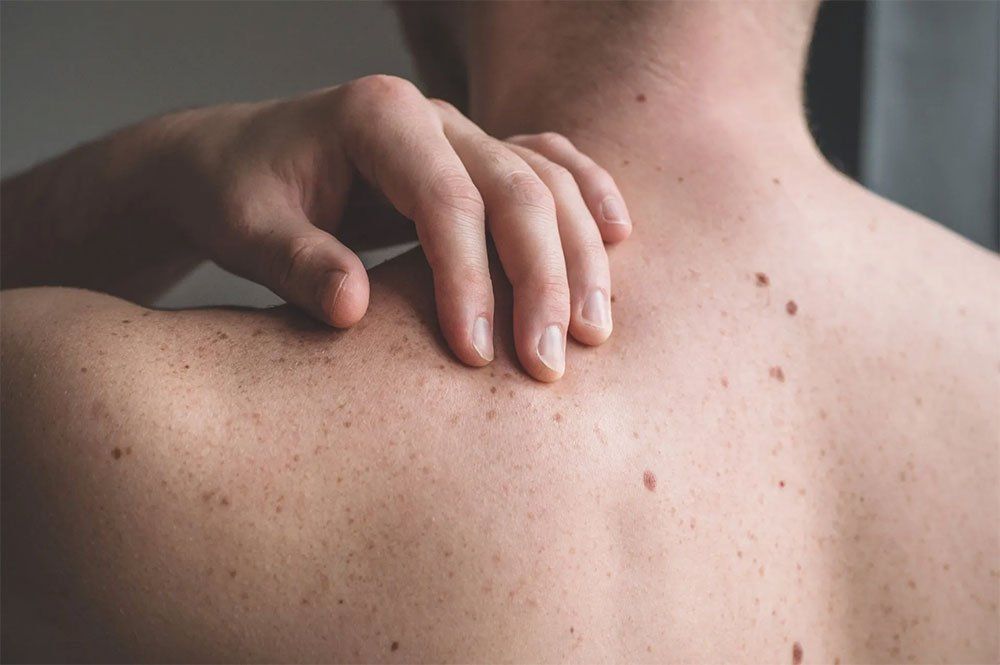
Your body is protected by your skin, which helps prevent damage to internal tissues and infection. However, the skin isn't impervious to disease and infection, and skin conditions are common at all stages of life. If you would like to learn more about your skin, check out these four skin diseases and conditions that are common in adults.
Skin tags develop in almost one-half of the adult population. While these elevated skin growths don't pose any significant health hazards, they can prove both uncomfortable and embarrassing, depending on their location. Fortunately, a qualified dermatologist can remove your unsightly skin tags safely and easily.
Lines around the eyes are almost impossible to hide. Makeup can sometimes make them more noticeable, and sunglasses are not acceptable to wear everywhere. A more effective solution is to learn the little habits that cause the lines to begin or worsen existing wrinkles. Additionally, use these four inexpensive and easy ways to reduce the risk of crow's feet and fine lines.
Lupus is an autoimmune disorder. If you have lupus, your immune system targets your tissue and organs. Unfortunately, you may suffer from skin rashes as your immune system attacks your skin. In fact, skin problems occur in 66 percent of patients with lupus, as noted by the Lupus Foundation of America. Fortunately, a dermatologist can help you combat the skin issues that arise from this disorder.

Skin cancer is the most common cancer in the United States, affecting one in five people in their lifetime, according to the American Academy of Dermatology. While some types of skin cancer can be treated effectively, other types, particularly melanoma, can often be fatal. Take steps to prevent skin cancer and reduce your risk.